Cognitive Behavioural Coaching Starts 25 January 2024

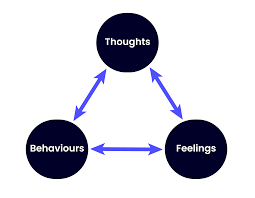
The power of CBC is that it engages the client on a conscious level to understand their limiting beliefs and the roadblocks that they face and then engages them actively in a thought-provoking and equal partnership to understand and identify unhelpful thinking and achieve their goals more effectively and with less risk of setbacks.
- This engagement is enforced through the coach’s ability to use Socratic questioning.
CBC has a few models that can be learnt and used on clients depending on the context. A model that tackles unhelpful thinking and behaviors based on this thinking and another one that identifies limiting beliefs and the emotions connected to them.
CBC also operates on a performance formula that motivates the client to aim to achieve their potential.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Cognitive Behavioral Coaching (CBC) are related approaches that share some similarities but have distinct differences in their goals, methods, and applications. Here’s an overview of the key differences:
- Primary Focus:
- CBT (Cognitive Behavioral Therapy): CBT is a form of psychotherapy primarily designed to treat mental health issues and emotional difficulties. It addresses problematic thoughts, emotions, and behaviors to help individuals manage and overcome various psychological disorders such as anxiety, depression, and phobias.
- CBC (Cognitive Behavioral Coaching): CBC, on the other hand, is focused on personal and professional development. It aims to enhance an individual’s performance, skills, and overall well-being by addressing cognitive and behavioral patterns. While it may touch on psychological issues, the main focus is on helping individuals achieve their goals and improve their lives.
- Context of Application:
- CBT: Typically delivered in a therapeutic setting by licensed mental health professionals, such as psychologists or counselors.
- CBC: Applied in coaching contexts, often delivered by trained coaches. It is commonly used in organizational settings, executive coaching, life coaching, and other areas where individuals seek improvement and growth.
- Time Frame:
- CBT: Can be a relatively structured and time-limited process, often involving a set number of sessions focused on specific issues or goals.
- CBC: Tends to be more flexible in terms of duration, with coaching relationships lasting as long as needed for the individual to achieve their goals.
- Client’s Role:
- CBT: The therapist takes on a more directive role, guiding the client through structured interventions to challenge and change negative thought patterns and behaviors.
- CBC: Coaching tends to be more collaborative, with the coach and client working together to identify goals, develop strategies, and make positive changes. The coach serves as a facilitator and supporter.
- Outcome Orientation:
- CBT: Emphasizes symptom reduction and the alleviation of psychological distress. Success is often measured by improvements in mental health symptoms.
- CBC: Focuses on achieving specific goals, enhancing performance, and fostering personal development. Success is often measured by the client’s progress toward their desired outcomes.
Cognitive Behavioural Coaching | Life Coaching Academy
Meet your trainer: Toleen Badawi
https://www.theexecutivemonk.com/
This workshop runs for 7 weeks every Thursday at 7pm AEST
Email info@lifecoachingacademy.edu.au for an enrollment form


